YouPorn - Targeting 200 Million Views a Day and Beyond

Update: Here's the video of the talk.
Erick Pickup, lead developer at YouPorn.com, presented their architecture in a talk titled Building a Website To Scale given at the ConFoo conference. As you might expect, YouPorn is a beast, streaming three full DVDs of video every second, handing 300K queries every second, and generating up to 15GBs of log data per hour.
Unfortunately, all we have are the slides of the talk, so this article isn’t as technical as I might like, there’s no visibility at all on the video handling for example, but we do get some interesting details.
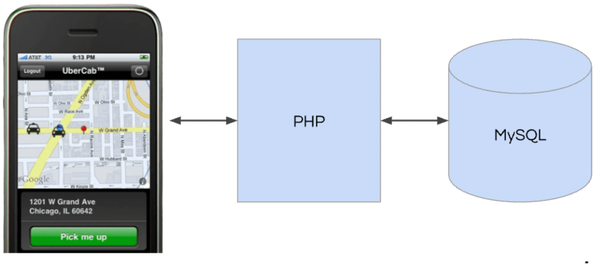
The most interesting takeway is that YouPorn is a pretty conventional LAMP stack, with a NoSQL twist as Redis now replaces MySQL in the live datapath. Reminds me a little of YouTube in its simplicity.
The second most interesting takeaway was the great switchover. Common wisdom says never rewrite, but in 2011 YouPorn rewrote their entire site to use PHP + Redis instead of a complex Perl + MySQL based architecture. And by all accounts the switchover went well. The site is 10% faster and they moved over 6 years of legacy data with no down time.
Read on to learn more about the YouPorn architecture...
Stats
- Launched in 2006, acquired in 2011.
- 100 million page views a day in 2008
- 300K queries / sec
- 100 Gb/s - 3 full DVDs streamed every second
- Logs 8GB-15GB of data per hour
Stack
- Originally written in Perl (Catalyst application with a DBIx::Class backend)
- Now PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) - is an alternative PHP FastCGI
- HAProxy
- ActiveMQ
- Varnish
- Redis
- Nginx
- MySQL
- Syslog-ng
- Symfony2 - a PHP Web Development Framework.
Architecture
- The great switchover. The entire site was rewritten in 2011 to use PHP instead of a complex Perl architecture and Redis instead of MySQL and ActiveMQ.
- Targeted 200+ million daily requests
- Moved 6 years of legacy data without downtime
- New site is 10% faster.
- The process took longer than expected:
- Had to decide on which technologies to use
- Longer than expected learning curve
- Moving and restructuring data from MySQL to Redis
- Staffing
- HAProxy - provides load balancing, intelligent load distribution, and health checks
- Maintain two pools of servers: a write pool with a fail-over to backup-Master and a read pool will servers except the master.
- Varnish - reverse proxy helping speed up the site and reduce server load. Used also for cache management, edge side includes (ESIs), and health check on web servers.
- Syslog-ng - collects data on page views and is used for view counters and related videos.
- Nginx - high performance web server running PHP-FPM and acts as a external CDNs for static files like CSS, images and JS.
- Symfony - fast and feature rich, comes with a large set of libraries.
- Considers Symfony2 + Redis = Rapid Development + Scalable Website - a well balanced equation.
- Loves dependency injection.
- Choosing a web framework doesn't mean killing performances as long as you use a solid architecture in front of it.
- ActiveMQ - message bus designed for large sites, used for writes to MySQL and Redis.
- They found it too rigid for a site undergoing constant changes and the gains did not justify maintaining a separate Java infrastructure.
- Would like a do-over since the problems may have been more the developers than the tech.
- Redis - a fast, open source, KV store, now the primary data source.
- Updated in real-time.
- Sorted sets are used for all lists
- Pipelining, executing several Redis commands with a single atomic command, is key for performance
- After the switchover additional Redis nodes were added, not because Redis was overworked, but because the network cards couldn't keep up with Redis.
- All reads come from Redis
- MySQL is used to allow the building new sorted sets as requirements change.
- Append-only-file (AOF) format is used for incremental backups and is IO pain free
- Consider using Redis as temporary cache in front of a Redis persistent store as a way to improve performance and reduce load.
- MySQL - in a support role to feed Redis
- Highly normalized because it’s not used directly for the site.
- Some tables have 100+ million rows.
- Used to populate Redis lists with new features
- Both GIT and SVN are used, which doesn’t work well.
- Doctrine is used in their CMS. Great tool that has saved weeks of development.